"No scientific conclusion is ever final. But we can say we believe that the present theory of evolution, on the basis of massive accumulated evidence, at the moment is by far the best scientific explanation of the diversity of life that surrounds us."
"…evolution fits that highest accolade as well as does the theory of that the Earth circles the sun.
Evolution, like other scientific theories, is closer to meaning to 'fact' than it is to the common lay meaning of theory."
p. 57.
Terms | Key Ideas | Outline | Summary

Oak-savanna woodland, Pacific coast. This sort of plant association was probably the sort of habitat --if not deserts-- that our hominid ancestors developed within as the glaciating retreat or advances dried out the rain forests of Central and Southern Africa.
As the African plains began to dry-out millions of years ago forests became more scattered such as the trees seen here. Fewer heavy forested areas pressured simians, monkeys and apes to face sparser and sparser woodlands with less fruit and tubers to nourish their needs. Hominids descend from a line of arboreal (tree adjusted) apes that began to take to the ground and not the trees.
| Vocabulary
|
|
| origins & loss in descent, | ratio, |
| Archaeopteryx, | missing links, |
| Tiktaalik, | Paleolithic, |
| traits, | tool-making, |
| deep time, | Olduwan culture, |
| cultures, | society, |
| exodus, | rock-solid
|
![]() Pale Blue dot – by Carl Sagan-- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p86BPM1GV8M
Pale Blue dot – by Carl Sagan-- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p86BPM1GV8M
ideas
Š
Geological thousands
of centuries
Š
Genetic hundreds
of generations
Š
Acquired traits decades (epigenetic influences)
Natural
clocks and timing
Carbon &
Potassium Argon,
Palinology, or pollen grains in sediment analysis
Dendrochronoloy
(tree-ring) & ice core–Oxygen isotope–analysis
missing links the Wolemi pine, a 2 million year old ancestor {58
correspondence
of fossils and DNA evidence
The Origin of life { 56
The RNA world –chemosynthetic evidence
ribonucleic acid is a replicating molecular strand that may be a forerunner of DNA
i. “how
and where life itself began . . .remains unresolved” {56
ii. surface rocks exposed to UV radiation
vs. deep sea thermals
Fossil record { 58
1.
Fish-tetrapod ancestor {59-60
2.
“no such reversal in the fossil record”
{59
The human line { 60
i. Chimpanzees, our separation from that line 3 million years ago and the enigma of growing brain volumes.
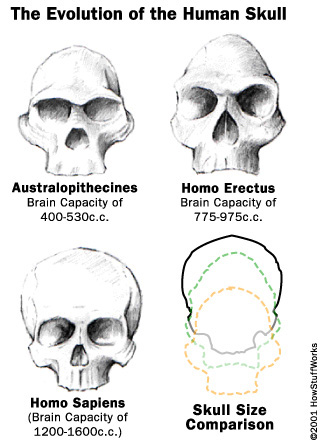
ii. Southern African Apes –
Taung child
1. Human family tree is a “bush”
- Ramapithecus
- Ardipithecus
- Australopithecus
- Homo habilis
- Homo erectus
- Homo sapiens Neanderthalensis
- Homo sapiens
"As you can see, the human family pole––the hominins (the technical term for
humans and their ancestors after they diverged from the chimpanzee line)–has in
the past fifty years become the 'family bush.' During much of the past , several
human species (hominin) were living at the same time."
pages 62-63.
2.7 million year old Hominid split with the Chimpanzees and pygmy or Bonobo chimpanzees.
page. 65.
 Homo afarensis and Homo neanderthalensis skulls differ in cranial capacity.
Homo afarensis and Homo neanderthalensis skulls differ in cranial capacity.
Fossil record of Culture { 66.
“Interestingly, there is a connection between the ability to make stone tools and the ability to speak. Chimps. . . . but they do not have the fine hand-eye coordination that would let them manufacture stone tools. . . . It turns out that the same kind of neuromuscular coordination required for stone tool manufacture is also essential to the ability of our tongues to undergo the incredible gymnastics that are required to produce speech.”
![]()
Earth Lawrence Berkeley lab
Hall of Human Origins; The American Museum of Natural History
Science, geology and biology on the internet
Geological time clock
versus the Geological time spiral